 |
GST Lead Base |
|
|
Home | Search | Contact us |
| :: Main Menu :: |
| Overview
Search Filarial Details Contact us |
 |
Filariasis
is a helminthic infection found principally in tropical and subtropical
areas in Africa, and in the South Pacific regions, it is caused by infection
with members of the Phylum Nemata Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi
and Brugia timori. The disease is transmitted from man through
several genera and species of mosquitoes. The acute disease is manifested
by recurrent chills and fever and by visible swelling or nodules of the
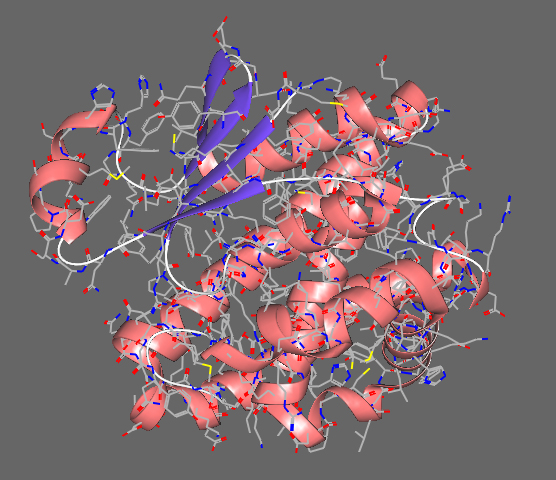
lymphatic system and redness of the overlaying skin due to parasitic involvement. The human filarial parasite Brugia malayi is an arthropod-borne nematode which causes lymphatic filariasis, an infection afflicting more than 120 million people worldwide. Glutathione S-transferase(s) (GST) enzyme from Brugia malayi has been exploited as a target in lymphatic filariasis therapeutics. An active GST is a homodimer of a 208 residue long monomer consisting of two domains, smaller a/ß domain and larger a domain. The components of the glutathione (GSH) system mainly GST enzymes are critical antioxidant and detoxification system responsible for the long-term existence of filarial worms in mammalian host hence they are major chemotherapeutic targets in filarial species. In the present study, fifty-five phytochemicals from ten plants predicted and reported to have potential nematicidal activity along with ADMET satisfaction have been docked to B. malayi GST enzyme to access their binding and consequently, their inhibitory activity. |
 |
Designed & Developed by Rosana O. B., Shaji A., Riju A., Reena N., Santhosh J Eapen and Shamina A. |